Susan Rogers Van Katwyk, York University, Canada
In late May, the latest version of the draft Pandemic Instrument, also referred to as the “pandemic treaty,” was shared with Member States at the World Health Assembly. The text was made available online via Health Policy Watch and it quickly became apparent that all mentions of addressing antimicrobial resistance in the Pandemic Instrument were at risk of removal.
Work on the Pandemic Instrument began in December 2021 after the World Health Assembly agreed to a global process to draft and negotiate an international instrument — under the Constitution of the World Health Organization (WHO) — to protect nations and communities from future pandemic emergencies.
Since the beginning of negotiations on the Pandemic Instrument, there have been calls from civil society and leading experts, including the Global Leaders Group on Antimicrobial Resistance, to include the so-called “silent” pandemic of antimicrobial resistance in the instrument.
Just three years after the onset of a global pandemic, it is understandable why Member States negotiating the Pandemic Instrument have focused on preventing pandemics that resemble COVID-19. But not all pandemics in the past have been caused by viruses and not all pandemics in the future will be caused by viruses. Devastating past pandemics of bacterial diseases have included plague and cholera. The next pandemic could be caused by bacteria or other microbes.
Antimicrobial resistance
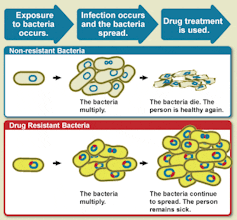
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is the process by which infections caused by microbes become resistant to the medicines developed to treat them. Microbes include bacteria, fungi, viruses and parasites. Bacterial infections alone cause one in eight deaths globally.
AMR is fueling the rise of drug-resistant infections, including drug-resistant tuberculosis, drug-resistant pneumonia and drug-resistant Staph infections such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). These infections are killing and debilitating millions of people annually, and AMR is now a leading cause of death worldwide.
Without knowing what the next pandemic will be, the “pandemic treaty” must plan, prepare and develop effective tools to respond to a wider range of pandemic threats, not solely viruses.
Even if the world faces another viral pandemic, secondary bacterial infections will be a serious issue. During the COVID-19 pandemic for instance, large percentages of those hospitalized with COVID-19 required treatment for secondary bacterial infections.
New research from Northwestern University suggests that many of the deaths among hospitalized COVID-19 patients were associated with pneumonia — a secondary bacterial infection that must be treated with antibiotics.
Treating these bacterial infections requires effective antibiotics, and with AMR increasing, effective antibiotics are becoming a scarce resource. Essentially, safeguarding the remaining effective antibiotics we have is critical to responding to any pandemic.
That’s why the potential removal of measures that would help mitigate AMR and better safeguard antimicrobial effectiveness is so concerning. Sections of the text which may be removed include measures to prevent infections (caused by bacteria, viruses and other microbes), such as:
- better access to safe water, sanitation and hygiene;
- higher standards of infection prevention and control;
- integrated surveillance of infectious disease threats from human, animals and the environment; and
- strengthening antimicrobial stewardship efforts to optimize how antimicrobial drugs are used and prevent the development of AMR.
The exclusion of these measures would hinder efforts to protect people from future pandemics, and appears to be part of a broader shift to water-down the language in the Pandemic Instrument, making it easier for countries to opt-out of taking recommended actions to prevent future pandemics.
Making the ‘pandemic treaty’ more robust
Measures to address AMR could be easily included and addressed in the “pandemic treaty.”
In September 2022, I was part of a group of civil society and research organizations that specialize in mitigating AMR who were invited the WHO’s Intergovernmental Negotiating Body (INB) to provide an analysis on how AMR should be addressed, within the then-draft text.
They outlined that including bacterial pathogens in the definition of “pandemics” was critical. They also identified specific provisions that should be tweaked to track and address both viral and bacterial threats. These included AMR and recommended harmonizing national AMR stewardship rules.
In March 2023, I joined other leading academic researchers and experts from various fields in publishing a special edition of the Journal of Medicine, Law and Ethics, outlining why the Pandemic Instrument must address AMR.
The researchers of this special issue argued that the Pandemic Instrument was overly focused on viral threats and ignored AMR and bacterial threats, including the need to manage antibiotics as a common-pool resource and revitalize research and development of novel antimicrobial drugs.
Next steps
While earlier drafts of the Pandemic Instrument drew on guidance from AMR policy researchers and civil society organizations, after the first round of closed-door negotiations by Member States, all of these insertions, are now at risk for removal.
The Pandemic Instrument is the best option to mitigate AMR and safeguard lifesaving antimicrobials to treat secondary infections in pandemics. AMR exceeds the capacity of any single country or sector to solve. Global political action is needed to ensure the international community works together to collectively mitigate AMR and support the conservation, development and equitable distribution of safe and effective antimicrobials.
By missing this opportunity to address AMR and safeguard antimicrobials in the Pandemic Instrument, we severely undermine the broader goals of the instrument: to protect nations and communities from future pandemic emergencies.
It is important going forward that Member States recognize the core infrastructural role that antimicrobials play in pandemic response and strengthen, rather than weaken, measures meant to safeguard antimicrobials.
Antimicrobials are an essential resource for responding to pandemic emergencies that must be protected. If governments are serious about pandemic preparedness, they must support bold measures to conserve the effectiveness of antimicrobials within the Pandemic Instrument.![]()
Susan Rogers Van Katwyk, Adjunct Professor, School of Global Health and Managing Director, AMR Policy Accelerator, York University, Canada
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.

